
Grounded in archival discoveries, Afterlives traces the origins of nineteenth-century America’s preservation compulsion, illuminating the influences of botanical, medical, spiritualist, and sentimental discourses on Whitman’s work. Tuggle unveils previously unrecognized connections between Whitman and the leading “medical men” of his era, such as the surgeon John H. Brinton, founding curator of the Army Medical Museum, and Silas Weir Mitchell, the neurologist who discovered phantom limb syndrome. Remains from several amputee soldiers whom Whitman nursed in the Washington hospitals became specimens in the Army Medical Museum.
Tuggle is the first scholar to analyze Whitman’s role in medically memorializing the human cadaver and its abandoned parts.


Elizabeth Hallam explores these museums, past and present, showing how they display the human body—whether naked, stripped of skin, completely dissected, or rendered in the form of drawings, three-dimensional models, x-rays, or films. She identifies within anatomy museums a diverse array of related issues—from the representation of deceased bodies in art to the aesthetics of science, from body donation to techniques for preserving corpses and ritualized practices for disposing of the dead. Probing these matters through in-depth study, Anatomy Museum unearths a strange and compelling cultural history of the spaces human bodies are made to occupy when displayed after death.


On March 8, 1782, a group of western settlers killed nearly one hundred unarmed and peaceful Indians who had converted to Christianity under the tutelage of missionaries from the Church of the United Brethren. The murders were cold-blooded and heartless; roughly two-thirds of those executed were women and children. Its brutality stunned Benjamin Franklin in far-away France. He wrote: “the abominable Murders committed by some of the frontier People on the poor Moravian Indians, has given me infinite Pain and Vexation. The Dispensations of Providence in this World puzzle my weak Reason. I cannot comprehend why cruel Men should have been permitted thus to destroy their Fellow Creatures.” Since that maelstrom of violence struck the small Indian village of Gnadenhutten, history has treated the episode as a simple morality tale. While there were ample incidents of good and evil on March 8, that summation does not explain what brought murderers and victims together on the banks of the Muskingum River in today’s Ohio. It was actually the culmination of a series of events among different Indian tribes, the British, Congressional authorities at Pittsburgh, the Pennsylvania militia, and key individuals, all of which are lost in contemporary explanations of the massacre.
Anatomy of a Massacre: The Destruction of Gnadenhutten, 1782 fills that void by examining the political maneuvering among white settlers, Continental officials, British officers, western Indian tribes, missionaries, and the Indians practicing Christianity that culminated in the massacre. Uniquely, it follows the developing story from each perspective, using first-person accounts from each group to understand how they saw and experienced the changes on the American frontier. Along the way it profiles some of the key individuals responsible for the way the war unfolded. It is a fresh look at an often mentioned, but seldom understood, episode in the American Revolution.



By analyzing a wide range of literary texts and films (including episodes from Twilight Zone, the fiction of Philip K. Dick, Kazuo Ishiguro’s novel Never Let Me Go, Metropolis, The Golem, Frankenstein, The Terminator, Iron Man, Blade Runner, and I, Robot), and going back to alchemy and to Aristotle’s Physics and De Anima, she tracks four foundational narrative elements in this centuries-old discourse— the fantasy of the artificial birth, the fantasy of the mechanical body, the tendency to represent artificial people as slaves, and the interpretation of artificiality as an existential trope. What unifies these investigations is the return of all four elements to the question of what constitutes the human.
This focused approach to the topic of the artificial, constructed, or mechanical person allows us to reconsider the creation of artificial life. By focusing on their historical provenance and textual versatility, Kakoudaki elucidates artificial people’s main cultural function, which is the political and existential negotiation of what it means to be a person.


In 2012, a team of Belgian scientists reported that they had been unable to replicate a canonical experiment in the field of psychology known as “priming.” The original experiment, performed by John Bargh in the nineties, had purported to show that words connoting old age unconsciously influenced—or primed—research subjects, causing them to walk more slowly. When subsequent researchers could not replicate these results, Nobel-winning psychologist Daniel Kahneman warned of a “train wreck looming” if Bargh and his colleagues could not address doubts about their work. Since then, the inability to replicate other well-known priming experiments has helped precipitate an ongoing debate over what has gone wrong in psychology, raising fundamental questions about the soundness of research practices in the field.
Anatomy of a Train Wreck offers the first detailed history of priming research from its origins in the early 1980s to its recent collapse. Ruth Leys places priming experiments in the context of contemporaneous debates over not only the nature of automaticity but also the very foundations of social psychology. While these latest discussions about priming have largely focused on methodology—including sloppy experimental practices, inadequate statistical methods, and publication bias—Leys offers a genealogy of the theoretical expectations and scientific paradigms that have guided and motivated priming research itself. Examining scientists’ intellectual strategies, their responses to criticism, and their assumptions about the nature of subjectivity, Anatomy of a Train Wreck raises crucial questions about the evidence surrounding unconscious influence and probes the larger stakes of the replication crisis: psychology’s status as a science.


Liberal: spoken in a certain tone, heard more and more often lately, it summons up permissiveness, materialism, rootlessness, skepticism, relativism run rampant. How has liberalism, the grand democratic ideal, come to be a dirty word? This book shows us what antiliberalism means in the modern world—where it comes from, whom it serves, and why it speaks with such a forceful, if ever-changing, voice.
In the past, in a battle pitting one offspring of eighteenth-century rationalism against another, Marxism has been liberalism’s best known and most vociferous opponent. But with the fall of Communism, the voices of ethnic particularism, communitarianism, and religious fundamentalism—a tradition Stephen Holmes traces to Joseph de Maistre—have become louder in rejection of the Enlightenment, failing to distinguish between the descendants of Karl Marx and Adam Smith. Holmes uses the tools of the political theorist and the intellectual historian to expose the philosophical underpinnings of antiliberalism in its nonmarxist guise. Examining the works of some of liberalism’s severest critics—including Maistre, Carl Schmitt, Leo Strauss, and Alasdair MacIntyre—Holmes provides, in effect, a reader’s guide to antiliberal culture, in all its colorful and often seductive, however nefarious, variety. As much a mindset as a theory, as much a sensibility as an argument, antiliberalism appears here in its diverse efforts to pit “spiritual truths” and “communal bonds” against a perceived cultural decay and moral disintegration. This corrosion of the social fabric—rather than the separation of powers, competitive elections, a free press, religious tolerance, public budgets, and judicial controls on the police—is what the antiliberal forces see as the core of liberal politics. Against this picture, Holmes outlines the classical liberal arguments most often misrepresented by the enemies of liberalism and most essential to the future of democracy.
Constructive as well as critical, this book helps us see what liberalism is and must be, and why it must and always will engender deep misgivings along with passionate commitment.

"A splendid analysis of the centrality of architecture in the daily lives of the Batammaliba and its integral role in articulating social values....The story is beautifully told in the best of anthropological traditions."—Judith R. Blau, Contemporary Society
"A remarkable study....Blier's volume carries the study of African architecture to a qualitatively new level of scholarship. It introduces a new dimension whereby the architectural medium can be used to illuminate much of the entire belief system of any culture."—Labelle Prussin, African Arts
"In this excellent book Blier provides a richly detailed and searching account of what architecture means to the Batammaliba of northern Togo and Benin....The finest account I have yet read of the relations between systems of beliefs, ritual practices, and African aesthetics and plastic arts....The ethnography and basic insight should be the envy of any social anthropologist."—T.O. Beidelman, Man

During the Cultural Revolution, Mao exhorted the Chinese people to “smash the four olds”: old customs, old culture, old habits, and old ideas. Yet when the Red Guards in Tiananmen Square chanted “We want to see Chairman Mao,” they unknowingly used a classical rhythm that dates back to the Han period and is the very embodiment of the four olds. An Anatomy of Chinese reveals how rhythms, conceptual metaphors, and political language convey time-honored meanings of which Chinese speakers themselves may not be consciously aware, and contributes to the ongoing debate over whether language shapes thought, or vice versa.
Perry Link’s inquiry into the workings of Chinese reveals convergences and divergences with English, most strikingly in the area of conceptual metaphor. Different spatial metaphors for consciousness, for instance, mean that English speakers wake up while speakers of Chinese wake across. Other underlying metaphors in the two languages are similar, lending support to theories that locate the origins of language in the brain. The distinction between daily-life language and official language has been unusually significant in contemporary China, and Link explores how ordinary citizens learn to play language games, artfully wielding officialese to advance their interests or defend themselves from others.
Particularly provocative is Link’s consideration of how Indo-European languages, with their preference for abstract nouns, generate philosophical puzzles that Chinese, with its preference for verbs, avoids. The mind-body problem that has plagued Western culture may be fundamentally less problematic for speakers of Chinese.

William Miller embarks on an alluring journey into the world of disgust, showing how it brings order and meaning to our lives even as it horrifies and revolts us. Our notion of the self, intimately dependent as it is on our response to the excretions and secretions of our bodies, depends on it. Cultural identities have frequent recourse to its boundary-policing powers. Love depends on overcoming it, while the pleasure of sex comes in large measure from the titillating violation of disgust prohibitions. Imagine aesthetics without disgust for tastelessness and vulgarity; imagine morality without disgust for evil, hypocrisy, stupidity, and cruelty.
Miller details our anxious relation to basic life processes: eating, excreting, fornicating, decaying, and dying. But disgust pushes beyond the flesh to vivify the larger social order with the idiom it commandeers from the sights, smells, tastes, feels, and sounds of fleshly physicality. Disgust and contempt, Miller argues, play crucial political roles in creating and maintaining social hierarchy. Democracy depends less on respect for persons than on an equal distribution of contempt. Disgust, however, signals dangerous division. The high's belief that the low actually smell bad, or are sources of pollution, seriously threatens democracy.
Miller argues that disgust is deeply grounded in our ambivalence to life: it distresses us that the fair is so fragile, so easily reduced to foulness, and that the foul may seem more than passing fair in certain slants of light. When we are disgusted, we are attempting to set bounds, to keep chaos at bay. Of course we fail. But, as Miller points out, our failure is hardly an occasion for despair, for disgust also helps to animate the world, and to make it a dangerous, magical, and exciting place.


In this book, Dan Stanislawski studies the geography of various small towns in one Mexican state. He discusses the factors—landscape, buildings, culture groups, and so forth—that create a unique personality for each of these towns.

The Anatomy of Judgment was first published in 1990. Minnesota Archive Editions uses digital technology to make long-unavailable books once again accessible, and are published unaltered from the original University of Minnesota Press editions.
"The Anatomy of Judgment is a unique and valuable contribution to the literature of the social and humanistic contexts for science . . . The book will illuminate dark corners for any reader, and dozens of interesting points come to light." –Neil Greenberg, University of Tennessee
Tracing the emergence of science and the social institutions that govern it, The Anatomy of Judgment is an odyssey into what human thinking or judgment means. Philip Regal moves deftly from the history of Western philosophy to concepts of rationality in non-Western cultures, from the conceptual issues of the Salem witch trials to the basic structure of the human brain. The Anatomy of Judgment offers new perspectives on the workings of individual judgment and the social responsibility it entails.
Philip Regal is a professor of ecology and behavioral biology at the University of Minnesota. He served, during his pre- and postdoctoral work, as Coordinator's Appointee to the Mental Health Training Program at UCLA's Brain Research Institute.


At the core of Berlant's work is a three-part study of The Scarlet Letter, analyzing the modes and effects of national identity that characterize the narrator's representation of Puritan culture and his construction of the novel's political present tense. This analysis emerges from an introductory chapter on American citizenship in the 1850s and a following chapter on national fantasy, ranging from Hawthorne's early work "Alice Doane's Appeal" to the Statue of Liberty. In her conclusion, Berlant suggests that Hawthorne views everyday life and local political identities as alternate routes to the revitalization of the political and utopian promises of modern national life.



Building upon recent work in communication, social psychology, social cognition, and political science, Jacob Shamir and Michal Shamir approach public opinion as a multidimensional concept with a multitude of expressions. Public opinion is not comprised merely of a distribution of attitudes obtained in the polls. It also expresses and is expressed by a climate of opinion, expectations, public speeches and political actions, including aggregate distributions of individual values, beliefs, and attitudes. Often these different facets coincide, but they may also diverge. Public opinion can evolve along different dynamic paths; the nature of the information environment is a major factor in determining which dynamic path will be set in motion.
While social information and social construction are important in public opinion processes, major information events play a central role in moving public opinion and in constraining processes of social construction. In this book these postulates are explored on the micro and macro levels, but the focus is on public opinion dynamics at the system level: how the facets of public opinion respond to the variability in information technology. This is approached from different directions and with different parameters. The authors use as their case study Israeli public opinion on issues of peace and terrorism during the Intifada.
The Anatomy of Public Opinion will form an important part in the body of study on the role of information in public opinion processes. It will be of interest to students and scholars of political science, communication, public opinion, and political psychology.
Jacob Shamir is Lecturer of Communication and Journalism, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem. Michal Shamir is Associate Professor of Political Science, Tel Aviv University.

Speaking wisely and provocatively about the political economy of race, Glenn C. Loury has become one of our most prominent black intellectuals—and, because of his challenges to the orthodoxies of both left and right, one of the most controversial. A major statement of a position developed over the past decade, this book both epitomizes and explains Loury’s understanding of the depressed conditions of so much of black society today—and the origins, consequences, and implications for the future of these conditions.
Using an economist’s approach, Loury describes a vicious cycle of tainted social information that has resulted in a self-replicating pattern of racial stereotypes that rationalize and sustain discrimination. His analysis shows how the restrictions placed on black development by stereotypical and stigmatizing racial thinking deny a whole segment of the population the possibility of self-actualization that American society reveres—something that many contend would be undermined by remedies such as affirmative action. On the contrary, this book persuasively argues that the promise of fairness and individual freedom and dignity will remain unfulfilled without some forms of intervention based on race.
Brilliant in its account of how racial classifications are created and perpetuated, and how they resonate through the social, psychological, spiritual, and economic life of the nation, this compelling and passionate book gives us a new way of seeing—and, perhaps, seeing beyond—the damning categorization of race in America.

“Lifts and transforms the discourse on ‘race’ and racial justice to an entirely new level.”
—Orlando Patterson
“Intellectually rigorous and deeply thoughtful…An incisive, erudite book by a major thinker.”
—Gerald Early, New York Times Book Review
Why are black Americans so persistently confined to the margins of society? And why do they fail across so many metrics—wages, unemployment, income levels, test scores, incarceration rates, health outcomes? Known for his influential work on the economics of racial inequality and for pioneering the link between racism and social capital, Glenn Loury is not afraid of piercing orthodoxies and coming to controversial conclusions. In this now classic work, reconsidered in light of recent events, he describes how a vicious cycle of tainted social information helped create the racial stereotypes that rationalize and sustain discrimination, and suggests how this might be changed.
Brilliant in its account of how racial classifications are created and perpetuated, and how they resonate through the social, psychological, spiritual, and economic life of the nation, this compelling and passionate book gives us a new way of seeing—and of seeing beyond—the damning categorization of race.
“Paints in chilling detail the distance between Martin Luther King’s dream and the reality of present-day America.”
—Anthony Walton, Harper’s
“Loury provides an original and highly persuasive account of how the American racial hierarchy is sustained and reproduced over time. And he then demands that we begin the deep structural reforms that will be necessary to stop its continued reproduction.”
—Michael Walzer
“He is a genuine maverick thinker…The Anatomy of Racial Inequality both epitomizes and explains Loury’s understanding of the depressed conditions of so much of black society today.”
—New York Times Magazine


Beginning with the travels of Sir Robert’s father Sir William, the Paston wealth brought luxuries from across the globe to an idyllic retreat in rural Norfolk. There, the family commissioned Europe’s finest craftsmen to enhance their exotic rarities, a trove of objects that included everything from musical instruments to bejeweled ostrich eggs and nautilus shell goblets. The lavish hospitality of the Paston family was renowned throughout England, but the English Civil War and plague tore the country apart, and peace-loving Sir Robert was assailed by what he called a “whirlpool of misadventures.” As the dawn of the modern era saw the beginning of the family’s loss of fortune, Sir Robert kept faith and worked tirelessly to protect his wife and children. Encouraged by his friend Dr. Thomas Browne, he even found time to pursue his own idiosyncratic interests, employing both an alchemist in search of the Philosophers’ Stone and an artist to capture his favorite treasures in an enigmatic still life, The Paston Treasure. Exploring the Paston family’s history through their collection and this famed painting, The Anatomy of Riches offers a history of both early modern England and the modern world’s birth-pangs.

The guinea pig is so widely used in laboratories that it has become synonymous in common speech with "experimental animal." But until now there has been no complete and accurate anatomy of this otherwise familiar creature. Cavia has remained uncharted territory for experimenters who come to it without previous experience. Gale Cooper and Alan L. Schiller here provide a thorough description of guinea pig anatomy in a text illustrated with about four hundred separate drawings. It is a detailed, complete, and practical guide to the gross morphology of the animal. Nomenclature has been standardized according to the Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria.
The authors' dissections have been carefully correlated with the published literature on guinea pig anatomy, and numerous references are given. This book sets a new standard of beauty and clarity in anatomical illustration. Dr. Cooper's drawings not only provide anatomical information with the utmost in accuracy and fidelity, they are in themselves an aesthetic triumph. Her pencil drawings have been made by a technique that requires specially made paper and demands unusual skill from the artist; closely identified with the famous illustrator Max Brodl, this method is now rarely employed. Researchers in immunology, hematology, physiology, biochemistry, pharmacology, reproductive biology, comparative anatomy, and taxonomy, among other fields, will turn to this anatomy as a reliable guide to a favored experimental species.

The ambiguous intent of Henry James’s horror story The Turn of the Screw has fascinated and divided its readers since its publication in 1898. The division arises between the apparitionists and the nonapparitionists in interpretation of the plot and the characters. Thomas Mabry Cranfill and Robert Lanier Clark, Jr., have here taken up the argument and made an interpretation of their own.
The authors carefully considered the mountainous critical comment, studied James’s statements regarding his intent, and minutely scrutinized the story itself. After all this probing of opinions and following of clues and observing of human beings in action, they have come out strongly on the side of the nonapparitionists.
The authors base their conclusion on analyses of character, centrally that of the governess, whom they consider the protagonist of the fearsome drama, but peripherally those of Mrs. Grose, the children, the uncle in Harley Street, and even the deceased Miss Jessel and Peter Quint. Relentlessly they relate every episode, action, and speech to the character of the governess and her relationships with those around her at Bly, picturing her as a psychological “case” whose abnormal mental state brings to those around her the inescapable misery they all suffer.
The authors’ analysis unfolds as interestingly in terms of character and motive as if the reader did not already know what happens in James’s much-read story. It moves, moreover, with something of the same suspense as James’s horror tale, although the tension is intellectual rather than emotional. Each additional disclosure of evidence, the resolution of each situation, and the clarification of every puzzling ambiguity builds the analysis step-by-inevitable-step to its inescapable conclusion.
The style of the analysis is graceful, urbane, and witty. The introduction gives an excellent appraisal of literary comment on James’s story and an illuminating summary of the literary “war” over the meaning of it; the bibliography provides an impressive list of books and articles on this subject, annotated to indicate in what particular ways each makes a contribution to the controversy.


In 1543 the young and ambitious physician Andreas Vesalius published one of the most famous books in the history of medicine, On the Fabric of the Human Body. While we often think of dissection as destroying the body, Vesalius believed that it helped him understand how to construct the human body. In this book, Sachiko Kusukawa shows how Vesalius’s publication emerged from the interplay of Renaissance art, printing technology, and classical tradition. She challenges the conventional view of Vesalius as a proto-modern, anti-authoritarian father of anatomy through a more nuanced account of how Vesalius exploited cultural and technological developments to create a big and beautiful book that propelled him into imperial circles and secured his enduring fame.

This book is the first history of medieval European anatomical images. Richly illustrated, The Art of Anatomy in Medieval Europe explores the many ways in which medieval surgeons, doctors, monks, and artists understood and depicted human anatomy. Taylor McCall refutes the common misconception that Renaissance artists and anatomists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Andreas Vesalius were the fathers of anatomy who performed the first human dissections. On the contrary, she argues that these Renaissance figures drew upon centuries of visual and written tradition in their works.

Once upon a time, neuroscience was born. A dazzling array of neurotechnologies emerged that, according to popular belief, have finally begun to unlock the secrets of the brain. But as the brain sciences now extend into all corners of cultural, social, political, and economic life, a yet newer world has taken shape: “neuroculture,” which goes further than ever before to tackle the profound ethical implications we face in consequence.
The Assemblage Brain unveils a major new concept of sense making, one that challenges conventional scientific and philosophical understandings of the brain. Drawing on Deleuze and Guattari, Tony D. Sampson calls for a radical critical theory that operates in the interferences between philosophy, science, art, and politics. From this novel perspective the book is structured around two questions: “What can be done to a brain?” and “What can a brain do?” Sampson examines the rise of neuroeconomics in informing significant developments in computer work, marketing, and the neuropharmaceutical control of inattentiveness in the classroom. Moving beyond the neurocapitalist framework, he then reestablishes a place for proto-subjectivity in which biological and cultural distinctions are reintegrated in an understanding of the brain as an assemblage.
The Assemblage Brain unravels the conventional image of thought that underpins many scientific and philosophical accounts of how sense is produced, providing a new view of our current time in which capitalism and the neurosciences endeavor to colonize the brain.



A comprehensive account of the rise and fall of the mortgage-securitization industry, which explains the complex roots of the 2008 financial crisis.
More than a decade after the 2008 financial crisis plunged the world economy into recession, we still lack an adequate explanation for why it happened. Existing accounts identify a number of culprits—financial instruments, traders, regulators, capital flows—yet fail to grasp how the various puzzle pieces came together. The key, Neil Fligstein argues, is the convergence of major US banks on an identical business model: extracting money from the securitization of mortgages. But how, and why, did this convergence come about?
The Banks Did It carefully takes the reader through the development of a banking industry dependent on mortgage securitization. Fligstein documents how banks, with help from the government, created the market for mortgage securities. The largest banks—Countrywide Financial, Bear Stearns, Citibank, and Washington Mutual—soon came to participate in every aspect of this market. Each firm originated mortgages, issued mortgage-backed securities, sold those securities, and, in many cases, acted as their own best customers by purchasing the same securities. Entirely reliant on the throughput of mortgages, these firms were unable to alter course even when it became clear that the market had turned on them in the mid-2000s.
With the structural features of the banking industry in view, the rest of the story falls into place. Fligstein explains how the crisis was produced, where it spread, why regulators missed the warning signs, and how banks’ dependence on mortgage securitization resulted in predatory lending and securities fraud. An illuminating account of the transformation of the American financial system, The Banks Did It offers important lessons for anyone with a stake in avoiding the next crisis.

In 2020 the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft successfully landed on the surface of Bennu and collected pristine asteroid material for delivery to Earth in September 2023. Scientific studies of the samples, along with data collected during the rendezvous, promise to help find answers to some of humanity’s deepest questions: Where did we come from? What is our destiny in space?
This book, the world’s first complete (and stereoscopic) atlas of an asteroid, is the result of a unique collaboration between OSIRIS-REx mission leader Dante Lauretta and Brian May’s London Stereoscopic Company. Lauretta’s colleagues include Carina Bennett, Kenneth Coles, and Cat Wolner, as well as Brian May and Claudia Manzoni, who became part of the ultimately successful effort to find a safe landing site for sampling. The text details the data collected by the mission so far, and the stereo images have been meticulously created by Manzoni and May from original images collected by the OSIRIS-REx cameras.

In his latest book, David Bainbridge combines an otherworldly journey through the central nervous system with an accessible and entertaining account of how the brain's anatomy has often misled anatomists about its function. Bainbridge uses the structure of the brain to set his book apart from the many volumes that focus on brain function. He shows that for hundreds of years, natural philosophers have been interested in the gray matter inside our skulls, but all they had to go on was its structure. Almost every knob, protrusion, canal, and crease was named before anyone had an inkling of what it did--a kind of biological terra incognita with many weird and wonderful names: the zonules of Zinn, the obex ("the most Scrabble-friendly word in all of neuroanatomy"), the aqueduct of Sylvius, the tract of Goll.
This uniquely accessible approach lays out what is known about the brain (its structure), what we can hope to know (its function), and what we may never know (its evolution). Along the way Bainbridge tells lots of wonderful stories about the "two pounds of blancmange" within our skulls, and tells them all with wit and style.

The book will be a useful textbook for advanced ichthyology students as well as an encyclopedic source for those seeking a greater understanding of these fascinating creatures.


Birth figures are printed images of the pregnant womb, always shown in series, that depict the variety of ways in which a fetus can present for birth. Historian Rebecca Whiteley coined the term and here offers the first systematic analysis of the images’ creation, use, and impact. Whiteley reveals their origins in ancient medicine and explores their inclusion in many medieval gynecological manuscripts, focusing on their explosion in printed midwifery and surgical books in Western Europe from the mid-sixteenth to the mid-eighteenth century. During this period, birth figures formed a key part of the visual culture of medicine and midwifery and were widely produced. They reflected and shaped how the pregnant body was known and treated. And by providing crucial bodily knowledge to midwives and surgeons, birth figures were also deeply entangled with wider cultural preoccupations with generation and creativity, female power and agency, knowledge and its dissemination, and even the condition of the human in the universe.
Birth Figures studies how different kinds of people understood childbirth and engaged with midwifery manuals, from learned physicians to midwives to illiterate listeners. Rich and detailed, this vital history reveals the importance of birth figures in how midwifery was practiced and in how people, both medical professionals and lay readers, envisioned and understood the mysterious state of pregnancy.


The Book of Frogs commemorates the diversity and magnificence of all of these creatures, and many more. Six hundred of nature’s most fascinating frog species are displayed, with each entry including a distribution map, sketches of the frogs, species identification, natural history, and conservation status. Life-size color photos show the frogs at their actual size—including the colossal seven-pound Goliath Frog. Accessibly written by expert Tim Halliday and containing the most up-to-date information, The Book of Frogs will captivate both veteran researchers and amateur herpetologists.
As frogs increasingly make headlines for their troubling worldwide decline, the importance of these fascinating creatures to their ecosystems remains underappreciated. The Book of Frogs brings readers face to face with six hundred astonishingly unique and irreplaceable species that display a diverse array of adaptations to habitats that are under threat of destruction throughout the world.


In Charles Bell and the Anatomy of Reform, Carin Berkowitz takes readers into Bell’s world, helping us understand the life of medicine before the modern separation of classroom, laboratory, and clinic. Through Bell’s story, we witness the age when modern medical science, with its practical universities, set curricula, and medical professionals, was born.

The contemporary Cool attitude is barely 50 years old, but its roots are older than that. Cool Rules traces Cool's ancient origins in European, Asian, and African cultures, its prominence in the African-American jazz scene of the 1940s, and its pivotal position within the radical subcultures of the 1950s and '60s. Pountain and Robins examine various art movements, music, cinema, and literature, moving from the dandies and flâneurs of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries through to the expropriation of a whole cultural and psychological tradition by the media in the 1980s and '90s. What began as a rebellious posture adopted by minorities mutated to become mainstream itself. Cool is now primarily about consumption, as cynical advertisers have seized on it to create a constantly updated bricolage of styles and entertainments designed to affect the way people think about themselves and their society.

Through the stories of Duverney and Perrault, as well as those of Marin Cureau de la Chambre, Jean Pecquet, and Louis Gayant, The Courtiers' Anatomists explores the relationships between empiricism and theory, human and animal, as well as the origins of the natural history museum and the relationship between science and other cultural activities, including art, music, and literature.
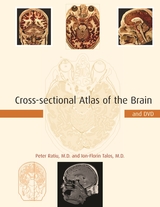
Cross-sectional Atlas of the Brain provides for the first time a set of high-resolution color cross-sections of the human brain (six times higher than that of the only complete data set available to date), each image accompanied by state-of-the-art MRI and CT scans of the same specimen. The sections were made at an interval of 147 micrometers of frozen tissue, virtually artifact free, with the blood vessels filled at sub-millimeter level. The more than two hundred detailed and fully annotated images in this atlas provide a complete body of reference to the gross anatomy of the brain. The accompanying line drawings of these images provide a roadmap for easy orientation.
The unparalleled resolution of the images also made it possible to derive cross-sections of the same specimen in all standard orientations--sagittal, coronal, and axial--through multi-planar computer-aided reformatting. This feature, which eliminates inter-subject variability, has never before been available in an anatomical atlas and makes the atlas especially useful for identifying and following anatomical structures in each plane. About the Companion DVD(View a sample in PDF format)
While the book itself contains 93 images (44 axial, 28 coronal, and 21 sagittal), the DVD contains the complete series of 1,481 axial images from one anatomic specimen from which the 44 axial images in the book were selected. These images were made at a resolution of 1525x1146 or 147 µm/pixel with a digital camera. The axial images are accompanied by 1,528 sagittal and 1,146 coronal images that were made by reformatting and reslicing the axial images. By placing these images side-by-side-by-side the DVD allows the user to see a particular region of the brain in all three orientations-axial, sagittal and coronal-simultaneously. These images are further accompanied by radiologic data. The DVD also allows the user to view a synchronized slide show of the images in all three planes. Images on the DVD that also appear in the book are highlighted with a blue background.
Cross-sectional Atlas of the Brain will be an essential reference for neuroscientists and clinicians (neurologists, radiologists, and neurosurgeons).

"Norman Polansky and his colleagues have produced a truly remarkable book. . . . One of the consequences of [the] relative invisibility of child neglect is that we also know less about it. But this book will help to correct that for it contains reports of findings from two systematic efforts to define, measure, classify, and understand child neglect."—Thomas M. Young, Social Service Review


For centuries, anatomy was a fundamental component of artistic training, as artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo sought to skillfully portray the human form. In Europe, illustrations that captured the complex structure of the body—spectacularly realized by anatomists, artists, and printmakers in early atlases such as Andreas Vesalius’s De humani corporis fabrica libri septem of 1543—found an audience with both medical practitioners and artists.
Flesh and Bones examines the inventive ways anatomy has been presented from the sixteenth through the twenty-first century, including an animated corpse displaying its own body for study, anatomized antique sculpture, spectacular life-size prints, delicate paper flaps, and 3-D stereoscopic photographs. Drawn primarily from the vast holdings of the Getty Research Institute, the over 150 striking images, which range in media from woodcut to neon, reveal the uncanny beauty of the human body under the skin.
This volume is published to accompany an exhibition on view at the Getty Research Institute at the Getty Center from February 22 to July 10, 2022.

Hands-on Anatomy targets undergraduate or graduate students who have completed an introductory anatomy course and are beginning to apply their anatomical knowledge to the human body, as well as healthcare professionals engaged in patient assessment and treatment. Organized by region of the body, chapters discuss skeletal landmarks, muscles, ligaments, and neurovascular structures, with a focus on how to palpate these structures. Additionally, guides on assessing the range of motion of joints are provided, along with descriptions of common clinical scenarios relating to each body area. The text is supplemented with images of skeletal landmarks and muscular anatomy, photos of surface landmarks and range of motion actives, and end-of-chapter review questions to ensure understanding and retention of what was described.

The definitive English edition of the “Father of Medicine.”
This is the ninth volume in the Loeb Classical Library’s ongoing edition of Hippocrates’ invaluable texts, which provide essential information about the practice of medicine in antiquity and about Greek theories concerning the human body. Here Paul Potter presents the Greek text with facing English translation of eleven treatises, four previously unavailable in English, that illuminate Hippocratic medicine in such areas as anatomy, physiology, prognosis and clinical signs, obstetrics, and ophthalmology.
The works available in the Loeb Classical Library edition of Hippocrates are:
Volume I: Ancient Medicine. Airs, Waters, Places. Epidemics 1 and 3. The Oath. Precepts. Nutriment.
Volume II: Prognostic. Regimen in Acute Diseases. The Sacred Disease. The Art. Breaths. Law. Decorum. Dentition.
Volume III: On Wounds in the Head. In the Surgery. On Fractures. On Joints. Mochlicon.
Volume IV: Nature of Man. Regimen in Health. Humors. Aphorisms. Regimen 1–3. Dreams.
Volume V: Affections. Diseases 1–2.
Volume VI: Diseases 3. Internal Affections. Regimen in Acute Diseases.
Volume VII: Epidemics 2 and 4–7.
Volume VIII: Places in Man. Glands. Fleshes. Prorrhetic 1–2. Physician. Use of Liquids. Ulcers. Haemorrhoids and Fistulas.
Volume IX: Anatomy. Nature of Bones. Heart. Eight Months’ Child. Coan Prenotions. Crises. Critical Days. Superfetation. Girls. Excision of the Fetus. Sight.
Volume X: Generation. Nature of the Child. Diseases 4. Nature of Women. Barrenness.
Volume XI: Diseases of Women 1–2.

The definitive English edition of the “Father of Medicine.”
This is the tenth volume in the Loeb Classical Library’s ongoing edition of Hippocrates’ invaluable texts, which provide essential information about the practice of medicine in antiquity and about Greek theories concerning the human body. Here, Paul Potter presents the Greek text with facing English translation of five treatises, four concerning human reproduction (Generation, Nature of the Child) and reproductive disorders (Nature of Women, Barrenness), and one (Diseases 4) that expounds a general theory of physiology and pathology.
The works available in the Loeb Classical Library edition of Hippocrates are:
Volume I: Ancient Medicine. Airs, Waters, Places. Epidemics 1 and 3. The Oath. Precepts. Nutriment.
Volume II: Prognostic. Regimen in Acute Diseases. The Sacred Disease. The Art. Breaths. Law. Decorum. Dentition.
Volume III: On Wounds in the Head. In the Surgery. On Fractures. On Joints. Mochlicon.
Volume IV: Nature of Man. Regimen in Health. Humors. Aphorisms. Regimen 1–3. Dreams.
Volume V: Affections. Diseases 1–2.
Volume VI: Diseases 3. Internal Affections. Regimen in Acute Diseases.
Volume VII: Epidemics 2 and 4–7.
Volume VIII: Places in Man. Glands. Fleshes. Prorrhetic 1–2. Physician. Use of Liquids. Ulcers. Haemorrhoids and Fistulas.
Volume IX: Anatomy. Nature of Bones. Heart. Eight Months’ Child. Coan Prenotions. Crises. Critical Days. Superfetation. Girls. Excision of the Fetus. Sight.
Volume X: Generation. Nature of the Child. Diseases 4. Nature of Women. Barrenness.
Volume XI: Diseases of Women 1–2.

This is the most comprehensive approach ever made to the human skeleton as a biological entity. It provides a holistic view, from the molecular and cellular level up to functional gross anatomy. The book synthesizes the latest research in a wide range of fields, including forensics, anthropology, cell biology, orthopedics, biomechanics, functional anatomy, and paleontology. Throughout the book the skeleton's functional and dynamic aspects are emphasized.
The first part of the book focuses on bone as living tissue: its composition, formation, growth and remodeling capabilities, and mechanical properties. The second part examines individual bones in the human body, combining strictly anatomical information with discussion of the major functions of each body section. For example, the chapter describing the axial skeleton is paired with one on the mechanics of breathing. The final part of the book surveys the archaeological and forensic applications of skeletal biology, including the estimation of age, sex, race, and stature; the effects of fracture and pathology on bone; and the modes of reconstructing skeletal remains. Elegant, detailed illustrations of the individual bones from several views and of the regions of the skeleton enhance the text.

Human Structure is an innovative introduction to human gross anatomy with a twofold approach to view the basics of anatomy from a broad scientific perspective and to explain the facts of form and function in terms and concepts that minimize the usual confusion and anxiety of beginning anatomy studies. Functional, comparative, and developmental anatomy are ingeniously woven into a single explanatory perspective, presenting human anatomy as an intelligible whole rather than as a heap of disconnected facts to be memorized. As a result, Human Structure is suitable not only for first-year medical students but also for undergraduates in premedical or biological science courses, for students in paramedical or college-level nursing programs, and indeed for anyone seeking a refresher course in human anatomy.
The book begins with the generalized segmental organization characteristic of vertebrates and then examines the most obviously segmented parts of the human body: the bones, muscles, vessels, and nerves of the trunk between the neck and the pelvis. The book progresses through regions where the simple organizational plan has undergone more and more radical modifications and ends with the ancient and extreme specializations found in the head. At each step, the authors widen our intellectual understanding of how these modifications have been imposed, onto-genetically or phylogenetically, upon simpler precursors.
The prose is personal and literate, peppered with inventive elucidations of concepts and accompanied by a wealth of illustrations designed for conceptual clarity and ease of visualization. The level of presentation has been finely tuned, over several years of class testing, to enhance its pedagogical effectiveness in human anatomy courses.


An Open Letters Monthly Best Nonfiction Book of the Year
America’s criminal justice system is broken. The United States punishes at a higher per capita rate than any other country in the world. In the last twenty years, incarceration rates have risen 500 percent. Sentences are harsh, prisons are overcrowded, life inside is dangerous, and rehabilitation programs are ineffective. Looking not only to court records but to works of philosophy, history, and literature for illumination, Robert Ferguson, a distinguished law professor, diagnoses all parts of a now massive, out-of-control punishment regime.
“If I had won the $400 million Powerball lottery last week I swear I would have ordered a copy for every member of Congress, every judge in America, every prosecutor, and every state prison official and lawmaker who controls the life of even one of the millions of inmates who exist today, many in inhumane and deplorable conditions, in our nation’s prisons.”
—Andrew Cohen, The Atlantic
“Inferno is a passionate, wide-ranging effort to understand and challenge…our heavy reliance on imprisonment. It is an important book, especially for those (like me) who are inclined towards avoidance and tragic complacency…[Ferguson’s] book is too balanced and thoughtful to be disregarded.”
—Robert F. Nagel, Weekly Standard


From reviews of previous editions:
“This is the standard reference about Texas mammals.” —Wildlife Activist
“A must for anyone seriously interested in the wildlife of Texas.” —Texas Outdoor Writers Association News
“[This book] easily fills the role of both a field guide and a desk reference, and is written in a style that appeals to the professional biologist and amateur naturalist alike. . . . [It] should prove useful to anyone with an interest in the mammal fauna of Texas or the southern Great Plains.” —Prairie Naturalist
The Mammals of Texas has been the standard reference since the first edition was coauthored by William B. Davis and Walter P. Taylor in 1947. Revised several times over the succeeding decades, it remains the most authoritative source of information on the mammalian wildlife of Texas, with physical descriptions and life histories for 202 species, abundant photographs and drawings, and distribution maps.
In this new edition, David J. Schmidly is joined by one of the most active researchers on Texas mammals, Robert D. Bradley, to provide a thorough update of the taxonomy, distribution, and natural history of all species of wild mammals that inhabit Texas today. Using the most recent advances in molecular biology and in wildlife ecology and management, the authors include the most current information about the scientific nomenclature, taxonomy, and identification of species, while also covering significant advances in natural history and conservation.

Building from author Alfredo Mirandé’s earlier work Rascuache Lawyer, the account is told by “The Professor,” who led a pro bono rascuache legal defense team comprising the professor, a retired prosecutor, and student interns, working without a budget, office, paralegals, investigators, or support staff. The book is a must-read for anyone interested in race, gender, and criminal injustice and will appeal not only to law scholars and social scientists but to lay readers interested in ethnographic field research, Latinx communities, and racial disparities in the legal system.
The case is presented as a series of letters to the author’s fictional alter-ego, Fermina Gabriel, an accomplished lawyer and singer. This narrative device allows the author to present the case as it happens, relaying the challenges and complexities as they occur and drawing the reader in.
While Ordinary Injustice deals with important, complicated legal issues and questions that arise in criminal defense work and looks at the case from the time of Juan’s arrest to the preliminary hearing, indictment, pretrial motions, and attempts to obtain a negotiated plea, it is written in nontechnical and engaging language that makes law accessible to the lay reader.

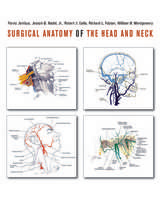
Surgical Anatomy of the Head and Neck was immediately hailed as indispensable when it was first published in 2001. In demand ever since, this classic surgical atlas—packed with more than 700 exceptional drawings, 537 of them in full color, by an internationally noted medical illustrator—is now available again, with an extensive new index, after years of being out of print.
Here is a surgeon’s-eye view of all anatomic details, from the upper thorax to the crown. Ideal for both surgery and test preparation, this volume features special boxed sections that focus on the surgical significance of each anatomical structure. Every illustration is clearly labeled with key anatomic landmarks, and a user-friendly design allows quick reference. This volume is an invaluable resource for surgeons, residents, and medical students.

On April 14, 1912, the Titanic struck an iceberg off Newfoundland. Taking more than 1,500 souls with her, Titanic sunk on what was intended to be the glorious maiden voyage of the biggest, most expensive, and most technologically advanced ship ever built.
In 1997, James Cameron’s Titanic, the most expensive and technologically advanced movie ever made, hit theaters. In 13 weeks, it became the highest-grossing film in North America, and shortly thereafter, the first motion picture to earn a billion dollars worldwide.
The cultural studies and film scholars who have contributed 13 essays to this collection ask the key question—Why? What made Titanic such a popular movie? Why has this film become a cultural and film phenomenon? What makes it so fascinating to the film-going public?
The articles address everything from the nostalgia evoked by the film to the semiotic meaningfulness created around “The Heart of the Ocean” diamond that figures so prominently as a symbol in the film. Contributors address questions of the representations of class, sexuality, and gender; analyze the cross-cultural reception of the film in nationally specific contexts; examine the impact of strategies for marketing the film through music; and cover the implications of the budget toward the film’s success. Finally, the contributors address the film’s multi-faceted relationship to genre, history, stardom, and contemporary social and economic means.

In The Trashing of Margaret Mead, Paul Shankman explores the many dimensions of the Mead-Freeman controversy as it developed publicly and as it played out privately, including the personal relationships, professional rivalries, and larger-than-life personalities that drove it. Providing a critical perspective on Freeman’s arguments, Shankman reviews key questions about Samoan sexuality, the alleged hoaxing of Mead, and the meaning of the controversy. Why were Freeman’s arguments so readily accepted by pundits outside the field of anthropology? What did Samoans themselves think? Can Mead’s reputation be salvaged from the quicksand of controversy? Written in an engaging, clear style and based on a careful review of the evidence, The Trashing of Margaret Mead illuminates questions of enduring significance to the academy and beyond.


Aileen Douglas draws on feminist and other new theoretical perspectives to reassess Smollett's entire body of fiction as well as his classic Travels through France and Italy. Like many writers of his time, Douglas argues, Smollett was interested in the body and in how accurately it reflects internal disposition. But Smollett's special contribution to the eighteenth-century novel is his emphasis on sentience, or the sensations of the physical body. Looking at such works as The Adventures of Roderick Random, The Expedition of Humphry Clinker, The Adventures of Peregrine Pickle, and The History and Adventures of an Atom, Douglas explores the ways Smollett uses representations of sentience—especially torment and pain—in his critique of the social and political order.
Trained in medicine, Smollett was especially alert to the ways in which the discourses of medicine, philosophy, and law construct (as we would put it now) the body as an object of knowledge, and yet his work always returns to the importance of the physical world of the body and its feelings. Smollett reminds us, as Douglas aptly puts it, that "if you prick a socially constructed body, it still bleeds."

In June 2008, the rivers of eastern Iowa rose above their banks to create floods of epic proportions; their amazing size—flowing in places at a rate nearly double that of the previous record flood—and the rapidity of their rise ruined farmlands and displaced thousands of residents and hundreds of businesses. In Cedar Rapids, the waters inundated more than nine square miles of the downtown area; in Iowa City, where the flood was also the most destructive in history, the University of Iowa’s arts campus was destroyed. By providing a solid base of scientific and technical information presented with unusual clarity and a wealth of supporting illustrations, the contributors to this far-reaching book, many of whom dealt firsthand with the 2008 floods, provide a detailed roadmap of the causes and effects of future devastating floods.
The twenty-five essays fall naturally into four sections. “Rising Rivers, Spreading Waters” begins by comparing the 2008 floods with the midwestern floods of 1993, moves on to trace community responses to the 2008 floods, and ends by illuminating techniques for forecasting floods and determining their size and frequency. “Why Here, Why Now?” searches for possible causes of the 2008 floods and of flooding in general: annual crops and urban landscapes, inflows into and releases from reservoirs, and climate change. “Flood Damages, Flood Costs, Flood Benefits” considers the complex mix of flood costs and effects, emphasizing damages to cities and farmlands as well as potential benefits to natural communities and archaeological sites. “Looking Back, Looking Forward” lays out approaches to managing the floods of the future that are sure to come.
While the book draws most of its examples from one particular region, it explains flooding throughout a much larger region—the midwestern Corn Belt—and thus its sobering yet energizing lessons apply well beyond eastern Iowa. By examining the relationships among rivers, floodplains, weather, and modern society; by stressing matters of science and fact rather than social or policy issues; and by addressing multiple environmental problems and benefits, A Watershed Year informs and educates all those who experienced the 2008 floods and all those concerned with the larger causes of flooding.

Opening with an accessible rundown of cetacean biology—including the most recent science on feeding, mating, and communication—Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises then presents species-specific natural history on a range of topics, from anatomy and diet to distribution and conservation status. Each entry also includes original drawings of the species and its key identifiers, such as fin shape and color, tooth shape, and characteristic markings as they would appear both above and below water—a feature unique to this book.
Figures of myth and—as the debate over hunting rages on—figures of conflict since long before the days of Moby-Dick, whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also ecologically important and, in many cases, threatened. Written for general enthusiasts, emergent cetacean fans, and biologists alike, this stunning, urgently needed book will serve as the definitive guide for years to come.
READERS
Browse our collection.
PUBLISHERS
See BiblioVault's publisher services.
STUDENT SERVICES
Files for college accessibility offices.
UChicago Accessibility Resources
home | accessibility | search | about | contact us
BiblioVault ® 2001 - 2025
The University of Chicago Press









